Dental Radiology
We are here to help when you need us.

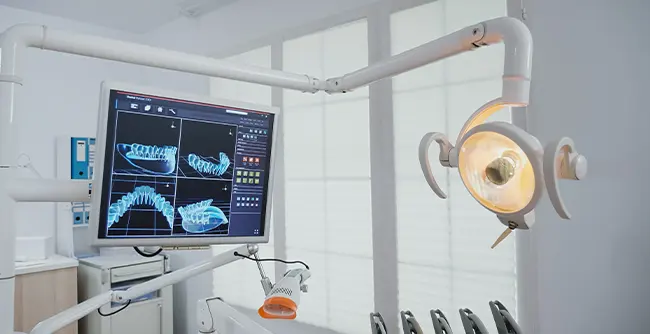
Dental radiology, also known as dental radiography or oral radiology, is a branch of radiology that focuses on the use of various imaging techniques to capture images of the teeth, jaws, and surrounding oral structures. These images are essential for diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of dental and oral health conditions. Dental radiology encompasses a range of imaging methods, each with its specific applications and advantages. Here are some of the key aspects of dental radiology:
1. Intraoral Radiography:** This is the most common type of dental radiography and involves taking X-ray images of the teeth and adjacent structures. Intraoral X-rays are used for detecting cavities, evaluating the health of tooth roots, and assessing the bone structure surrounding the teeth. The two primary types of intraoral X-rays are periapical (which captures the entire tooth, including the root) and bitewing (which shows the crowns of upper and lower teeth in a specific area).
2. Extraoral Radiography:** Extraoral radiography captures images of the larger oral and facial structures, including the jawbone and the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This type of imaging is useful for orthodontic treatment planning and assessing the overall health and structure of the jaw and skull. Common extraoral X-rays include panoramic radiographs and cephalometric radiographs.
3. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT):** CBCT is a specialized imaging technique that provides three-dimensional images of the oral and maxillofacial region. It is particularly valuable for implant planning, orthodontic treatment, and diagnosing complex dental conditions.
4. Digital Radiography:** Digital X-ray technology has largely replaced traditional film-based radiography in dentistry. Digital radiography allows for faster image acquisition, lower radiation exposure, and easy storage and retrieval of images. It is widely used in both intraoral and extraoral dental imaging.
5. Safety and Radiation Protection:** Dental professionals take specific precautions to minimize radiation exposure to patients during X-ray procedures. Lead aprons, thyroid collars, and high-speed film or digital sensors are commonly used to protect the patient while obtaining diagnostic images.
6. Diagnostic Value:** Dental radiography is critical for diagnosing a wide range of oral health issues, including cavities, gum disease, impacted teeth, jaw fractures, tumors, and infections. It aids in creating treatment plans and monitoring the progress of dental treatments.
7. Pediatric Dentistry:** Dental radiography is also commonly used in pediatric dentistry. Specialized techniques, such as child-sized X-ray sensors and lower radiation doses, are used to ensure the safety of young patients.
Dental radiology plays a crucial role in modern dentistry by providing valuable diagnostic information to dentists and oral surgeons. It allows for the early detection and treatment of dental issues, contributing to improved oral health and overall well-being. Patients should feel free to discuss any concerns about radiation exposure with their dental care providers, who will ensure that all necessary precautions are taken during dental radiographic procedures.